Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial Cystitis
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also known as bladder pain syndrome (BPS), is a chronic condition characterized by recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and pelvic region. It is considered a complex disorder with an unknown cause and is more common in women than in men.
Symptoms of interstitial cystitis can vary from person to person but often include:
1. Pain and discomfort: Most individuals with IC experience chronic pelvic pain, often described as a pressure or burning sensation in the bladder. The pain may range from mild to severe and can fluctuate in intensity.
2. Urgency and frequency: People with IC often have a frequent and urgent need to urinate, even when the bladder contains a small amount of urine. This can lead to disrupted sleep patterns and a reduced quality of life.
3. Bladder pain during sexual intercourse: Many individuals with IC experience pain or discomfort during sexual activity, which can impact their sexual relationships.
4. Nocturia: The need to wake up multiple times during the night to urinate is common in people with interstitial cystitis.
The exact cause of interstitial cystitis is unknown, but several theories exist. Some possible factors that may contribute to the development of IC include abnormalities in the bladder lining, an autoimmune response, nerve dysfunction, genetic predisposition, or a combination of these factors. However, more research is needed to fully understand the condition.
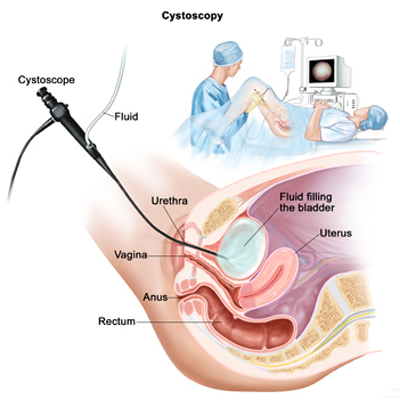
Diagnosing interstitial cystitis can be challenging because its symptoms overlap with other urinary tract disorders. Your doctor will likely perform a thorough evaluation, which may include a medical history review, physical examination, urine tests, cystoscopy (to examine the bladder), and other specialized tests to rule out other conditions.
While there is currently no cure for interstitial cystitis, treatment aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. Treatment options may include:
1. Lifestyle changes: Strategies such as dietary modifications (avoiding trigger foods and beverages like caffeine, alcohol, spicy foods), stress management techniques, and bladder training can help reduce symptoms.
2. Medications: Certain medications, such as oral medications (like pentosan polysulfate sodium) and bladder instillations (using medications directly into the bladder), may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
3. Physical therapy: Pelvic floor physical therapy can help relax and strengthen the pelvic floor muscles, which can provide relief for some individuals.
4.Nerve stimulation: Techniques like sacral nerve stimulation or bladder instillations with anesthetics can help manage symptoms in some cases.
It is essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop an individualized treatment plan tailored to your specific needs. They can provide guidance and support throughout your journey with interstitial cystitis.