Uro-Oncology
Uro-Oncology
Uro-oncology, also known as genitourinary oncology, is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of cancers affecting the urinary tract and male reproductive system. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra, while the male reproductive system includes the prostate, testicles, and penis.
Uro-oncologists are medical professionals who specialize in the management of urological cancers, which primarily include prostate cancer, bladder cancer, kidney cancer, testicular cancer, and penile cancer. They work closely with other specialists, such as urologists, medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, radiologists, and pathologists, to provide comprehensive and multidisciplinary care to cancer patients.
Here is some information about the common urological cancers:
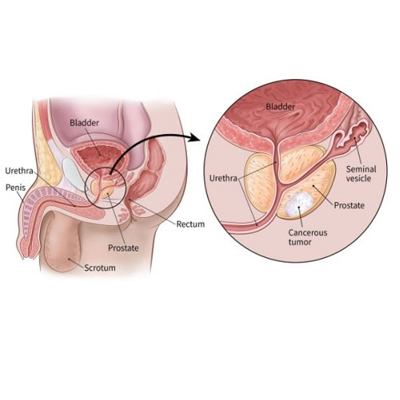
Prostate Cancer: Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men. Uro-oncologists play a crucial role in the early detection, staging, and treatment of prostate cancer. Treatment options may include active surveillance, surgery (prostatectomy), radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy.
Bladder Cancer: Bladder cancer typically affects the lining of the bladder. Uro-oncologists are involved in diagnosing and treating bladder cancer. Treatment options may include surgery (transurethral resection of the bladder tumor or cystectomy), radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy.
Kidney Cancer: Kidney cancer usually originates in the kidneys and can spread to other parts of the body. Uro-oncologists are involved in diagnosing kidney cancer and determining the most appropriate treatment approach. Treatment options may include surgery (nephrectomy), targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and radiation therapy.
Testicular Cancer: Testicular cancer typically affects younger men and is highly treatable, even in advanced stages. Uro-oncologists are involved in the diagnosis and treatment of testicular cancer. Treatment options may include surgery (radical orchiectomy), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and surveillance.
Penile Cancer: Penile cancer is a rare form of cancer that affects the penis. Uro-oncologists work with other specialists to diagnose and manage penile cancer. Treatment options may include surgery (partial or total penectomy), radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Uro-oncologists employ a personalized approach to cancer treatment, considering factors such as the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and their preferences. They aim to provide the most effective treatment while minimizing side effects and maintaining the patient's quality of life.
It's important to consult with a qualified uro-oncologist or a multidisciplinary team of specialists for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized management plan if you or someone you know is dealing with a urological cancer.