Prostate Surgery
Prostate Surgery
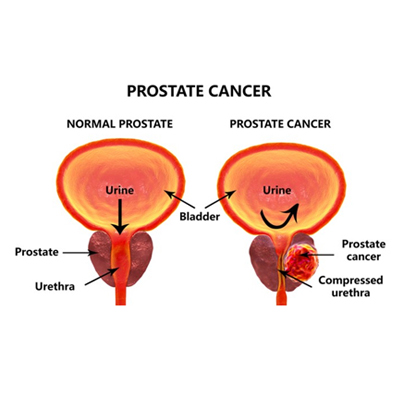
Prostate surgery, also known as prostatectomy, is a surgical procedure performed to remove all or part of the prostate gland. The prostate is a small gland located below the bladder in men, and it surrounds the urethra, the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body.
There are different reasons why prostate surgery may be necessary. The most common reasons include:
1. Prostate cancer: If cancer is confined to the prostate gland and has not spread, surgery may be performed to remove the entire prostate gland, known as a radical prostatectomy.
2. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH): BPH is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland that can cause urinary problems. Surgery may be recommended if medication and other treatments fail to relieve symptoms.
3. Prostatitis: This refers to inflammation of the prostate gland, often caused by infection. In some cases, if conservative treatments are ineffective, surgery may be considered.
There are different approaches to prostate surgery, and the choice depends on various factors such as the patient's condition, the surgeon's expertise, and the specific goals of the surgery. The common surgical techniques for prostate surgery include:
1. Open prostatectomy: This is the traditional surgical approach where a single incision is made in the lower abdomen to access and remove the prostate gland.
2. Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted prostatectomy: These minimally invasive techniques involve multiple small incisions and the use of specialized instruments and a camera to perform the surgery. Robotic-assisted surgery provides the surgeon with enhanced precision and dexterity.
3. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP): This procedure is primarily used to treat BPH. A surgical instrument called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra, and excess prostate tissue is removed.
The choice of surgical technique depends on various factors such as the patient's overall health, the size of the prostate gland, the presence of cancer, and the surgeon's expertise. Each technique has its own advantages and potential risks.
After prostate surgery, patients may experience a recovery period that includes some discomfort and temporary side effects such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction. However, these side effects are often temporary, and many patients regain normal urinary and sexual function over time. It is important to follow the post-operative instructions provided by the surgical team and attend follow-up appointments for proper recovery and monitoring.
It's worth noting that medical practices and techniques may evolve over time, so it's always best to consult with a healthcare professional or urologist for the most up-to-date and accurate information regarding prostate surgery.